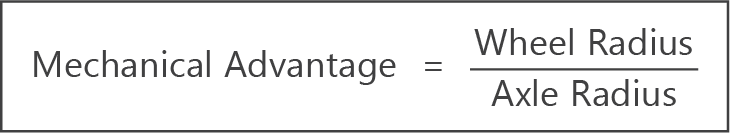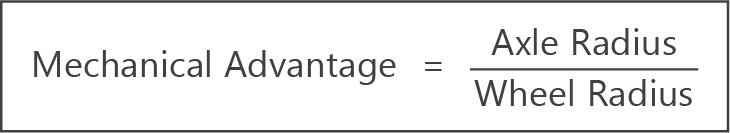This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn how wheels and axles and pulleys provide mechanical advantage.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe a wheel and axle and explain how it provides mechanical advantage.
- Discuss how a wheel and axle can be considered as a lever.
- Explain how wheels and axles can be force multipliers or speed multipliers, with examples.
- Describe a pulley and explain how it provides mechanical advantage.
- Compare fixed pulleys, movable pulleys and compound pulleys.
- Discuss how a pulley can be considered as a lever.

(Image: Bru-nO, Pixabay)
Lesson Summary
- A wheel and axle consists of a circular structure, known as the wheel, attached to a shaft or rod, known as the axle.
- The wheel and the axle have the same rotational speed but different linear speeds.
- When a wheel causes an axle to rotate:
- The wheel and axle functions as a class 2 lever.
- The wheel and axle is a force multiplier.
- When an axle causes a wheel to rotate:
- The wheel and axle functions as a class 3 lever.
- The wheel and axle is a speed multiplier.
- For a wheel and axle that is a class 2 lever, mechanical advantage is given by the formula:
- Mechanical advantage will always be greater than 1.
- For a wheel and axle that is a class 3 lever, mechanical advantage is given by the formula:
- Mechanical advantage will always be less than 1.
- A pulley is a special type of wheel and axle that consists of a rope or other material that passes around the outer surface of the wheel.
- A fixed pulley is a pulley that stays in the same position.
- It functions as a class 1 lever.
- Fixed pulleys always have a mechanical advantage of 1.
- They do not increase a force, but do change its direction.
- A movable pulley is a pulley that moves with a load.
- It functions as a class 2 lever.
- Movable pulleys always have a mechanical advantage of 2.
- They increase a force, but do not change its direction.
- A simple pulley consists of a single wheel.
- Its mechanical advantage depends on whether it is a fixed or movable pulley.
- A compound pulley consists of two or more wheels connected by a single rope.
- Its mechanical advantage is equal to the total number of rope sections that are supporting individual pulleys.
(Image: Tama66, Pixabay)
(Header image: spiritofamerica, Adobe Stock)