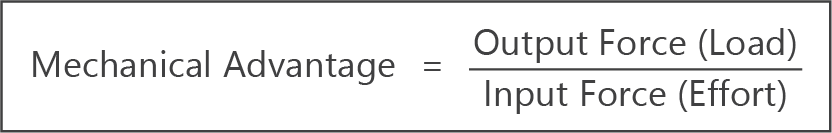This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn how simple machines make tasks easier by reducing the amount of effort required.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe what a simple machine is and name the six types of simple machines identified by early scientists.
- Explain how simple machines make tasks easier, but with a trade-off between output force and output distance.
- Define ‘work’ and calculate the work done by a simple machine.
- Define ‘mechanical advantage’ and calculate the mechanical advantage of a simple machine.
- Define ‘efficiency’ and calculate the efficiency of a simple machine.
- Compare simple machines and complex machines.

(Image: LubosHouska, Pixabay)
Lesson Summary
- A simple machine is a basic mechanical device that makes a task easier to perform.
- Simple machines include:
- Inclined planes
- Wedges
- Screws
- Levers
- Wheels and axles
- Pulleys
- Simple machines increase the magnitude of an applied force, thereby reducing the amount of force (effort) required to perform a task.
- The trade-off is that there is a decrease in the distance that the target object is moved.
- Work is the application of a force over a given distance.
- It can be calculated using the formula:
- Work is measured in joules (J).
- When a simple machine is used to perform a task, there is no difference in the amount of work done.
- Mechanical advantage is a measure of how much easier a task is to perform when using a machine.
- It can be calculated using the formula:
- Mechanical advantage has no units.
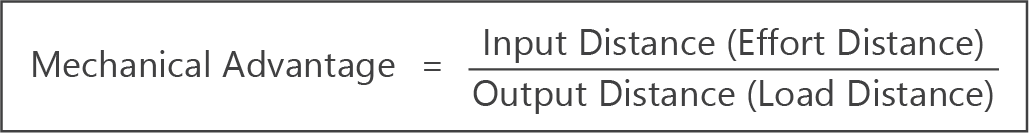
- Since force and distance are inversely proportional, mechanical advantage can also be calculated using the formula:
- Efficiency is a measure of how effectively a simple machine transfers input energy to output energy.
- It can be calculated using the formula:
- Efficiency is expressed as a percentage.
- A complex machine (compound machine) is a mechanical device consisting of two or more simple machines.
- The mechanical advantage of a complex machine can be calculated using the formulas above or by multiplying the mechanical advantages of each simple machine.

(Image: beprop, Pixabay)
(Header image: evkaz, Adobe Stock)