This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn how heat energy is transferred between substances by the processes of conduction, convection and radiation.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Differentiate between heat energy and temperature.
- Define heat transfer.
- Explain how the processes of conduction, convection and radiation transfer heat energy, using examples.
- Describe thermal conductors and thermal insulators, and give examples of each.
- Explain how substances transmit, absorb and reflect infrared radiation differently.

(Image: BlenderUnknown, Pixabay)
Lesson Summary
- The heat energy (thermal energy) of a substance is a measure of the total kinetic energy of all particles within that substance.
- It has the units joules (J) or calories (cal).
- Heat energy is related to the amount and type of substance.
- The temperature of a substance is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles within that substance.
- It has the units degrees Celsius (°C), degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or Kelvin (K).
- Temperature is unrelated to the amount and type of substance.
- We experience temperature as hot and cold, which we detect via thermoreceptors in our skin.
- Temperature can be measured using a thermometer.
- Heat transfer (heat flow) is the movement of heat from an area of high temperature to an area of low temperature.
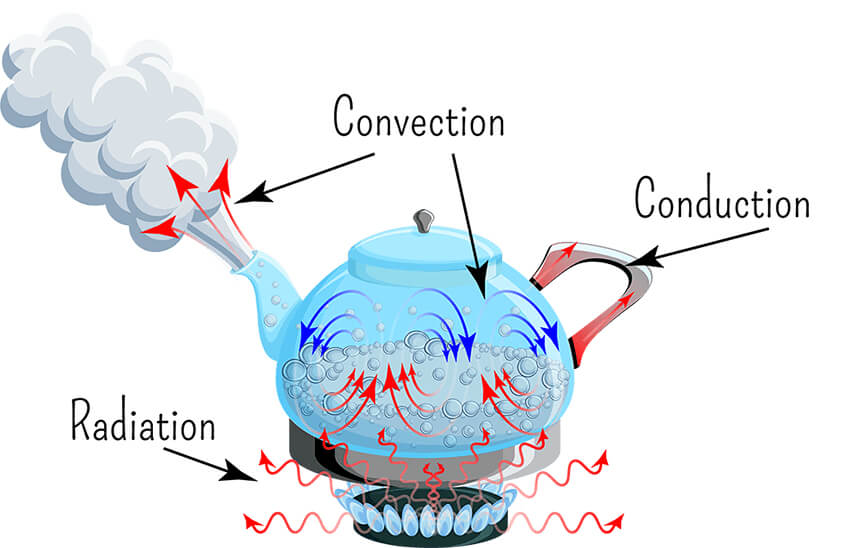
- Heat transfer can take place three ways – by conduction, convection and radiation.
- Conduction is the transfer of heat energy via particle collisions within a substance or between substances that are in contact with each other.
- Thermal conductors are materials that readily transfer heat by conduction.
- Thermal insulators are materials that do not readily transfer heat by conduction.
- Convection is the transfer of heat energy via the flow of fluids (liquids and gases), known as convection currents.
- Radiation is the transfer of heat energy via the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, especially infrared radiation, but also visible light, UV light and microwaves.
- The degree of absorption of infrared radiation by a substance is affected by its composition and colour.
- Transparent and translucent substances mostly transmit radiation.
- Dark, opaque substances mostly absorb radiation.
- Light, opaque substance mostly reflect radiation.
(Image: Inna, Adobe Stock)
(Header image: davit85, Adobe Stock)
