This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn how gear drives, belt drives and chain drives transfer forces and motion.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Explain what is meant by ‘mechanical power transmission’.
- Describe gear drives, belt drives and chain drives and discuss how they can be considered as special types of wheels and axles.
- Calculate the mechanical advantage of gear drives, belt drives and chain drives.

(Image: JRJfin, Adobe Stock
Lesson Summary
- Mechanical power transmission is the transfer of mechanical energy from one place to another.
- Gears, belt drives and chain drives are mechanical devices that transfer circular motion from one place to another.
- They consist of two or more connected wheels and axles that rotate about separate axes.
- A gear consists of a wheel with indented teeth.
- A belt drive (belt-driven pulley) consists of two wheels connected by a belt that wraps around both wheels.
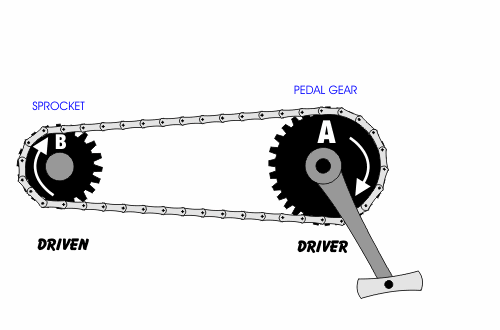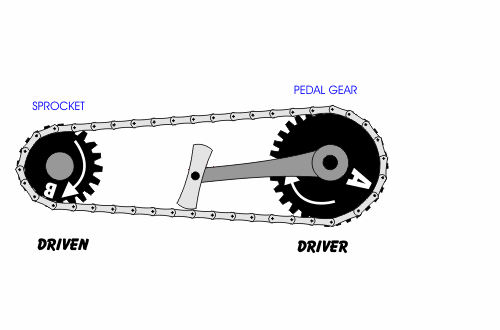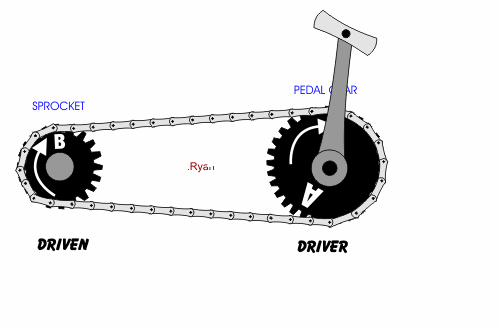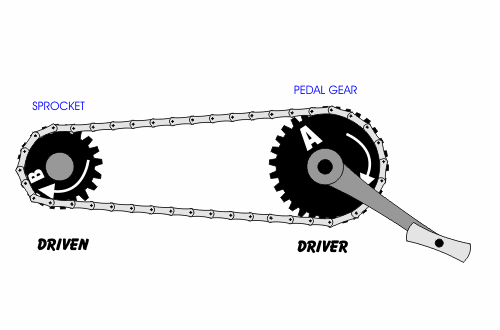
- A chain drive (chain-driven pulley) consists of two wheels connected by a chain that wraps around both wheels.
- In each case, a driver gear or driver pulley causes the rotation of a driven gear or driven pulley.
- Wheels in interlocking gears, belt drives and chain drives have the same linear speed, but a larger wheel will have a slower rotational speed than a smaller wheel.
- If a larger wheel drives a smaller wheel, the system is a speed multiplier.
- If a smaller wheel drives a larger wheel, the system is a force multiplier.
- The mechanical advantage of gears, belt drives and chain drives is given by the formula:
- Gears cause a change in direction of rotation.
- Belt drives and chain drives may or may not cause a change in direction of motion, depending in whether they are in the cross or open configuration.
(Image: Giphy)
(Header image: toptodown, Adobe Stock)

