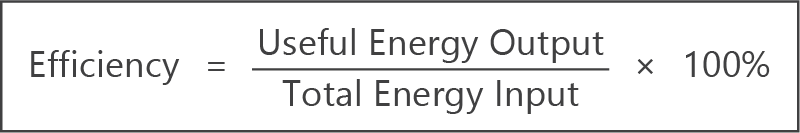This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the transfer, transformation and conservation of energy.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- State the law of conservation of energy.
- Differentiate between ‘energy transfer’ and ‘energy transformation’, with examples.
- Compare mechanical potential energy and kinetic energy in terms of energy transfer and transformation.
- Describe the relationship between potential energy and kinetic energy in an isolated mechanical system.
- Calculate the efficiency of energy transfer or transformation.
- Discuss why energy transfers and transformation cannot be 100% efficient.

(Image: jatocreate, Pixabay)
Lesson Summary
- The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be transferred between objects or converted into different forms.
- Energy transfer is the movement of energy from one location to another, without a change in the form of energy.
- Energy transformation is the conversion of energy from one form to another.
- Potential energy:
- Cannot be transferred between objects.
- Can only be transformed into kinetic energy.
- Kinetic energy:
- Can be transferred between objects.
- Can be transformed into several different forms of energy.
- In an isolated mechanical system:
- If an object’s kinetic energy increases, its potential energy decreases.
- If an object’s potential energy increases, its kinetic energy decreases.
- Whenever energy is transferred or transformed, some of that energy is ‘lost’.
- The efficiency of energy transfer or transformation is a measure of how much ‘useful’ energy is retained.
- Efficiency can be calculated using the formula:

(Image: Stefan Kühn; Wikimedia Commons)
(Header image: vladakela, Adobe Stock)