This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the different types of electromagnetic radiation, how they are produced and how they can be used.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe an electromagnetic wave and the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Identify the different types of electromagnetic radiation.
- Give examples of natural sources of the different types of electromagnetic radiation.
- Give examples of uses of the different types of electromagnetic radiation.

(Image: GDJ, Pixabay)
Lesson Summary
- An electromagnetic wave (also known as electromagnetic radiation) consists of an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating together as two transverse waves that are perpendicular to each other.
- Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light.
- The electromagnetic spectrum includes all types of electromagnetic radiation, with a range of frequencies and wavelengths.
- From lowest to highest frequency, the different types of electromagnetic radiation are:
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared light / infrared radiation
- Visible light
- Ultraviolet (UV) light / UV radiation
- X-rays
- Gamma rays / gamma radiation
- All objects emit electromagnetic radiation.
- The hotter the object, the higher the frequency of the radiation emitted.
- Electromagnetic waves with higher frequencies (shorter wavelengths) have higher energy and greater penetrating power.
- Gamma rays, X-rays and high frequency UV light are examples of ionising radiation – radiation that has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms and molecules. All other types of electromagnetic radiation are non-ionising.
- Biological effects of exposure to high energy radiation include sunburn and cancer.
- Examples of applications of the different types of electromagnetic radiation include:
- Radio waves – radio, television, mobile phones, mobile broadband, satellites, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Microwaves – microwave ovens, mobile phones, mobile broadband, WiFi, Bluetooth, satellites, radar, radio astronomy.
- Infrared light – heat detection, thermal imaging cameras (infrared cameras).
- Visible light – vision, photosynthesis.
- Ultraviolet light – vitamin D synthesis, fluorescence, sterilisation.
- X-rays – radiography, radiotherapy.
- Gamma rays – radiography, radiotherapy.
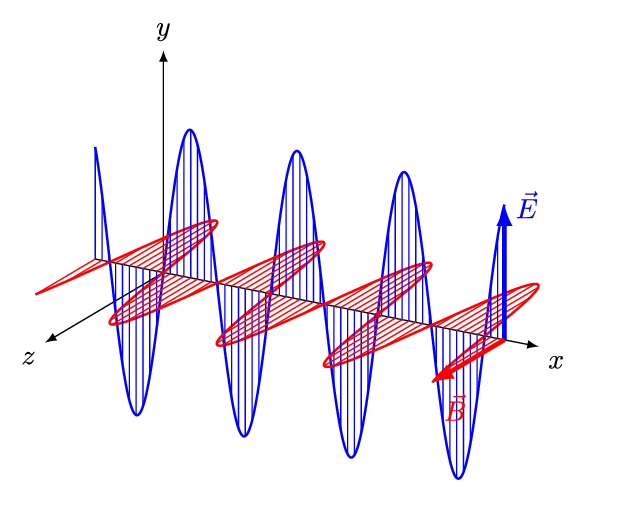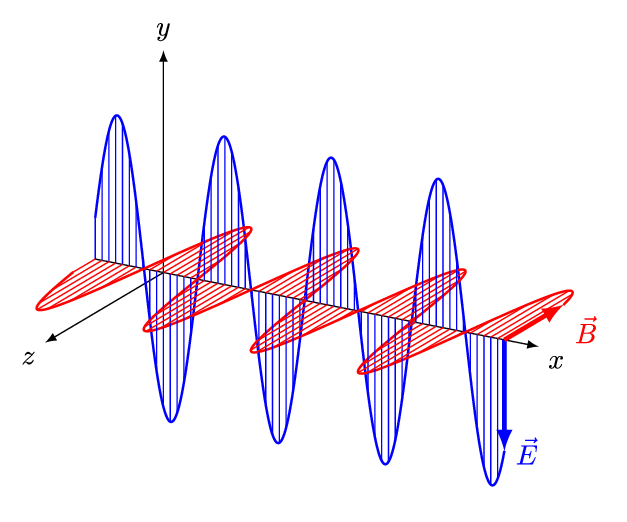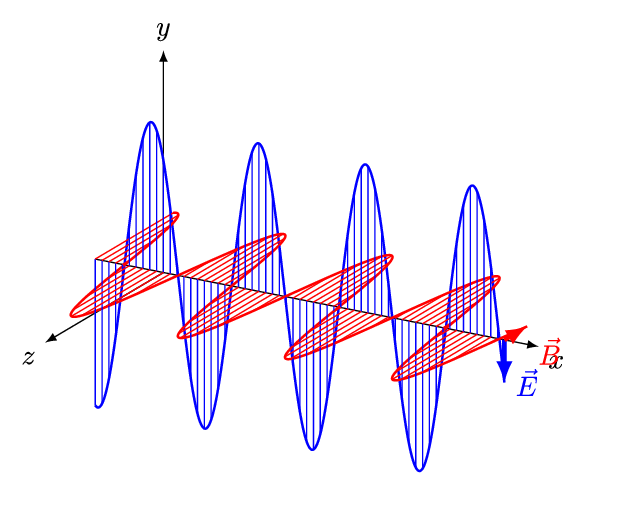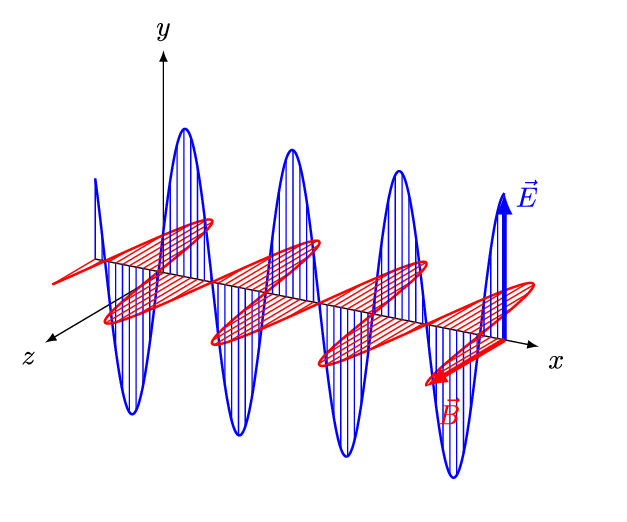
(Image: And1mu, Wikimedia Commons)
(Header image: FR Design, Adobe Stock)
