This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the formation and naming of ionic and covalent compounds.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe how ionic compounds and covalent compounds are formed.
- Write the chemical names and formulas for ionic and covalent compounds.
- Distinguish between ionic and covalent compounds based on their names or formulas.
- Draw structures for simple covalent compounds.
(Image: bobyramone, Adobe Stock)
Lesson Summary
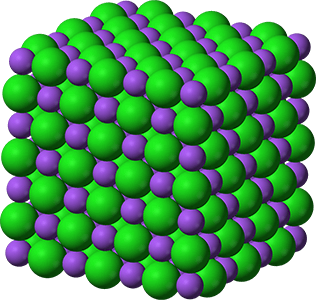
- Compounds can be divided into two main groups: ionic compounds and covalent compounds.
- Ionic compounds consist of positive ions and negative ions, joined by ionic
bonds.
- Ionic bonds are electrostatic forces of attraction between positive and negative ions.
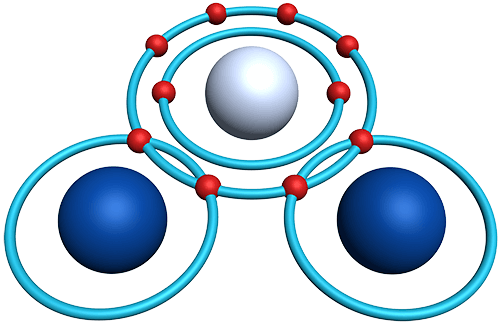
- Covalent compounds consist of non-metal atoms, joined by covalent bonds.
- Covalent bonds result from the sharing of valence electrons between atoms.
- A single covalent bond involves the sharing of one pair of electrons.
- A double covalent bond involves the sharing of two pairs of electrons.
- A triple covalent bond involves the sharing of three pairs of electrons.
- Ionic compounds are named after the ions that form them.
- The names of the positive and negative ions are joined together to form the compound name.
- Covalent compounds are named after the atoms that form them.
- The names of the two atoms are joined together to form the compound name.
- The ending of the second atom’s name is changed in the same way as for negative ions.
- The number of each type of atom is included in the name, using the prefixes mono, di, tri…
(Image: Benjah-bmm27, Wikimedia Commons)
(Header image: Benjah-bmm27, Wikimedia Commons)