This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn how matter can be categorised based on the subunits making it up, and how this affects the separability of substances.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe atoms and molecules.
- Compare pure substances and mixtures.
- Compare elements and compounds.
- Discuss the separation of elements, compounds and mixtures.

(Image: angelo.gi, Adobe Stock)
Lesson Summary
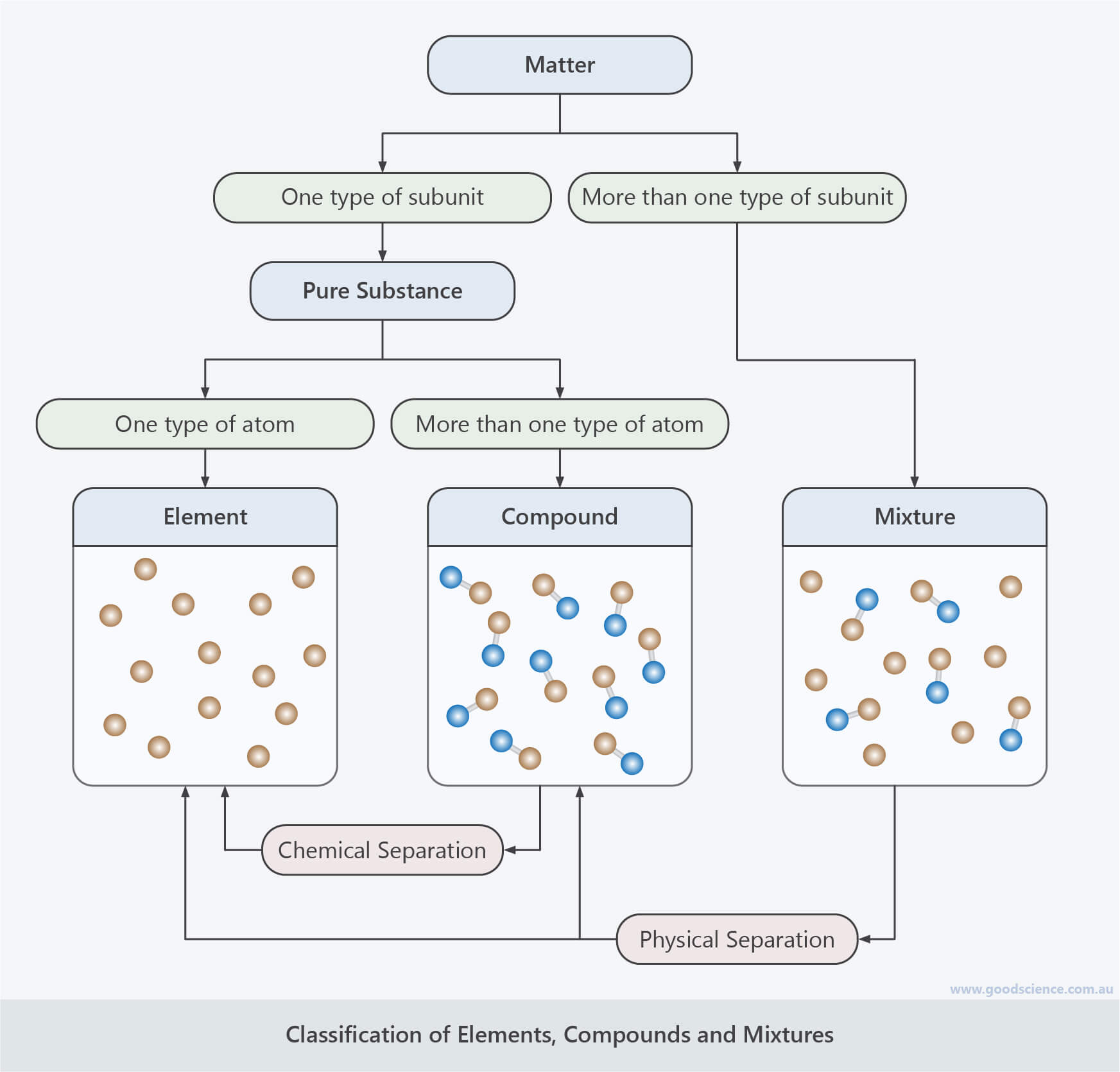
- There are two main types of subunits that make up matter: atoms and molecules.
- Atoms are the most basic type of subunit.
- Molecules consist of two or more atoms held in a fixed arrangement by chemical bonds.
- Matter can be classified into pure substances or mixtures, based on the number of different subunits it contains.
- Pure substances are made up of one type of subunit.
- Mixtures are made up of more than one type of subunit.
- Pure substances can be classified into elements or compounds, based the number of different atoms they contain.
- Elements are made up of one type of atom.
- Compounds are made up of more than one type of atom.
- Pure substances (elements and compounds) have fixed properties.
- Mixtures have variable properties.
- Elements cannot be separated into other substances.
- Compounds can be chemically separated into their component elements.
- Mixtures can be physically separated into their component substances.
(Header image: fresnel6, Adobe Stock)
