This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the six types of changes in state of matter, and the energy changes that are associated with them.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Name and describe the six changes of state.
- Use the particle model to explain the different changes of state in terms of heat energy.
- Define melting point and boiling point.
- Distinguish between boiling and evaporation.
(Image: MicroOne, Adobe Stock)
Lesson Summary
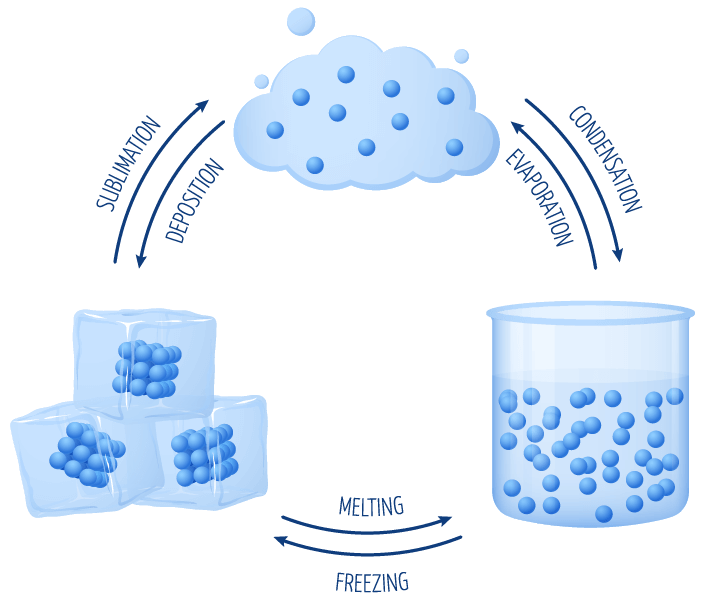
- There are six different types of state changes:
- Melting – when a substance changes from a solid to a liquid.
- Freezing – when a substance changes from a liquid to a solid.
- Vaporisation – when a substance changes from a liquid to a gas.
- Condensation – when a substance changes from a gas to a liquid.
- Sublimation – when a substance changes from a solid directly to a gas.
- Deposition – when a substance changes from a gas directly to a solid.
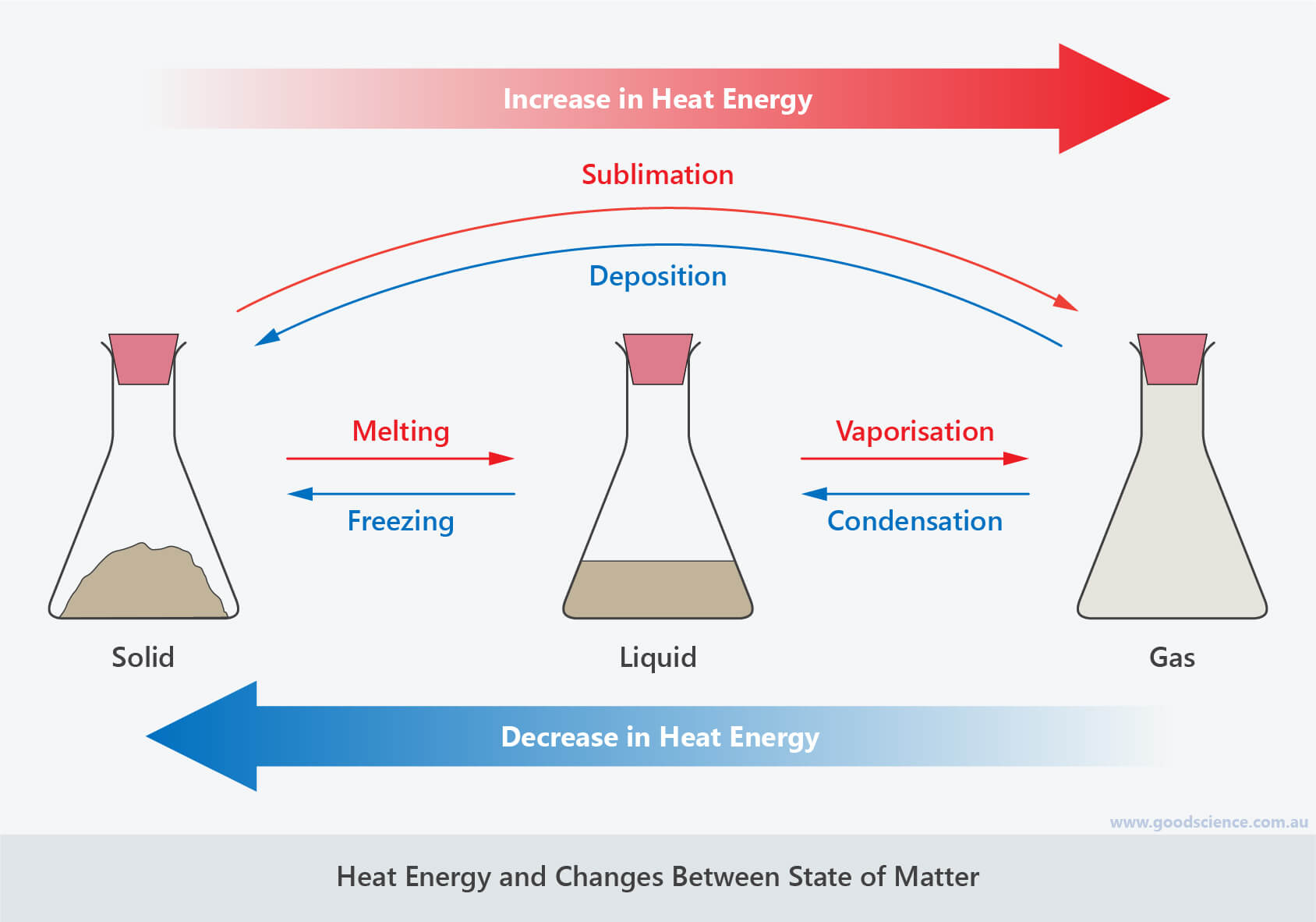
- Changes in state can be explained by the particle model in terms of heat energy.
- They involve the transfer of heat energy between particles and the surrounding environment.
- Melting, vaporisation and sublimation involve a gain of heat energy by particles.
- Heat energy is transferred from the surrounding environment to the particles.
- Condensation, freezing and deposition involve a loss of heat energy from particles.
- Heat energy is transferred from the particles to the surrounding environment.
- The melting/freezing point of a substance is the temperature at which it melts/freezes.
- The boiling/condensation point of a substance is the temperature at which it boils/condenses.
(Header image: skeeze, Pixabay)