This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the different ways atoms are arranged in pure substance – elements and compounds.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe elements and compounds.
- Describe atoms, molecules and lattices.
- Illustrate the different ways atoms can be arranged in elements, with examples.
- Illustrate the different ways atoms can be arranged in compounds, with examples.
(Image: Anna, Adobe Stock)
Lesson Summary
- Atoms are the fundamental subunits of matter.
- They may exist individually (in some elements) or joined to other atoms by chemical bonds, forming molecules or lattices (in most elements and all compounds).
- Molecules are discrete structures containing two or more atoms bonded together in a fixed arrangement.
- Molecules can consist of one type of atom, or more commonly, more than one type of atom.
- Lattices are continuous networks of atoms joined by chemical bonds.
- As with molecules, lattices can consist of one type of atom, or more commonly, more than one type of atom.
- Elements and compounds are both pure substances as they are made up of one type of chemical subunit.
- Elements are composed of one type of atom.
- These atoms may exist separately, as molecules or as a lattice.
- Compounds are composed of more than one type of atom.
- These atoms may exist as molecules or as a lattice.
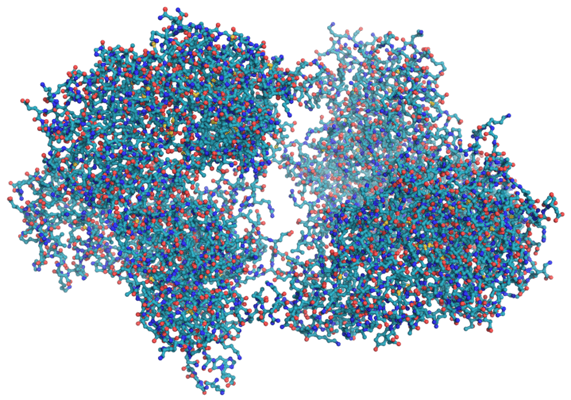
Some molecules, such as proteins, can contain thousands of atoms.
(Image: Splette, Wikimedia Commons)
(Header image: Anusorn, Adobe Stock)
