This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the structure and function of the nervous system.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe the general function of the nervous system.
- Describe the basic structure of neurons and the function of the three main types.
- Explain how nerve signals are transferred between neurons.
- Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system and describe their respective functions.
- Describe what a reflex arc is and explain how it enables rapid responses.
(Image: katestudio, Adobe Stock)
Lesson Summary
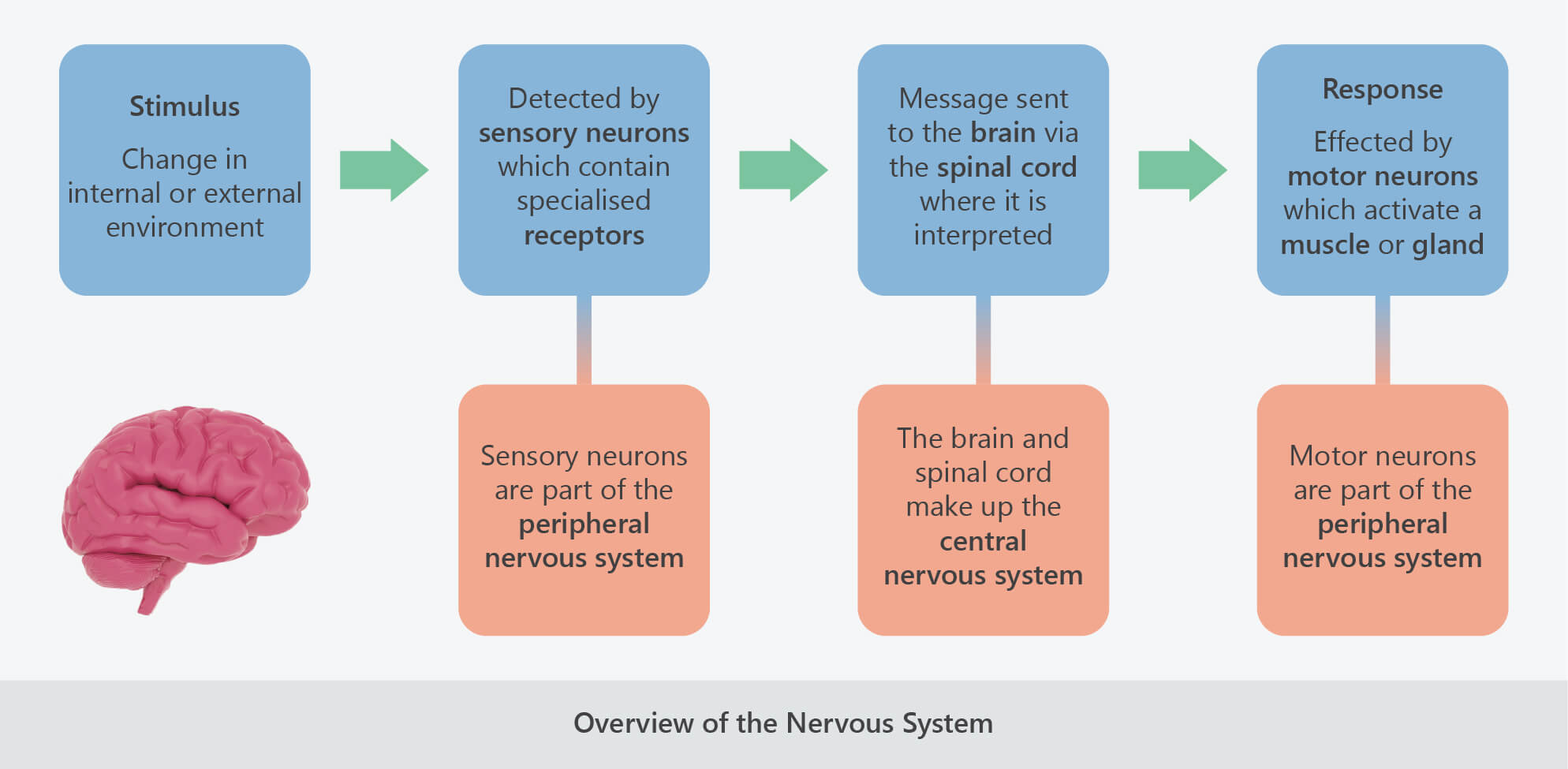
- The primary function of the nervous system is to monitor and respond to environmental changes.
- The nervous system is composed of nerve cells (neurons) which transmit electrical signals called nerve impulses.
- All nerve cells have three main components:
- Cell body – contains the nucleus and other cell organelles.
- Dendrites – receive nerve impulses from other nerve cells.
- Axon – sends nerve impulses to other nerve cells.
- Many axons and some dendrites are surrounded by an insulating layer called a myelin sheath.
- There are three functional types of nerve cells:
- Sensory neurons – detect changes in the environment.
- Motor neurons – effect a response in a muscle or gland.
- Interneurons – connect sensory neurons and motor neurons.
- A synapse is a small gap separating adjacent neurons.
- Neurotransmitters are molecules that carry a chemical signal across a synapse.
- The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
- It interprets sensory information and dictates responses.
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of all the nervous tissue that links the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
- It consists of sensory neurons, which detect changes, and motor neurons, which effect a response.
- Voluntary responses are carried out by the somatic nervous system.
- Involuntary responses are carried out by the autonomic nervous system.
- These include ‘fight or flight’ responses, which are controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, and ‘rest and digest’ responses, which are controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system.
- A reflex is a rapid, automatic response, in which a particular stimulus always causes the same motor response.
- It occurs via a reflex arc to and form the spinal cord, bypassing the brain.
(Header image: Giovanni Cancemi, Adobe Stock)