This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about excretion in humans, in particular, the urinary system.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Discuss the overall function of the excretory system.
- Describe different ways the human body removes waste.
- Describe the organs of the urinary system and discuss the role they play in excretion.
- Identify the main blood vessels flowing to and from the kidneys.
(Image: blueringmedia, Adobe Stock)
Lesson Summary
- Excretion refers to any process that eliminates metabolic waste products from the body.
- These materials would otherwise accumulate in the body and become toxic.
- The main excretory process that occur in the body are:
- Exhalation – the removal of carbon dioxide from the body via the lungs.
- Urination – the removal of urea from the body via the kidneys.
- Sweating – the removal of excess heat, salt and urea via glands in the skin.
- The excretory system incorporates several body systems – the respiratory system, the urinary system and the integumentary system.
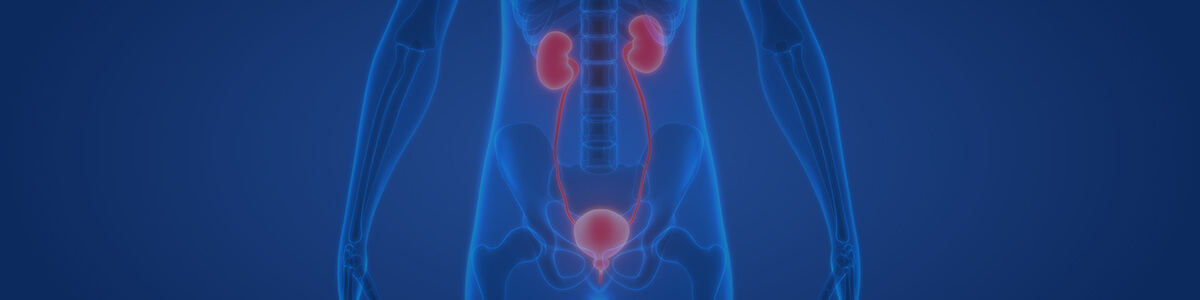
- The urinary system is a group of organs that remove urea and other metabolic wastes from the body as urine.
- Organs that make up the respiratory system are:
- The kidneys – the principal organs of the urinary system, that filter blood, separating waste products and removing them as urine.
- The ureters – long, thin tubes that transport urine from each kidney to the bladder.
- The bladder – a muscular pouch that stores urine; urethral sphincters at the base of the bladder control urination.
- The urethra – a tube that transports urine from the bladder out of the body.
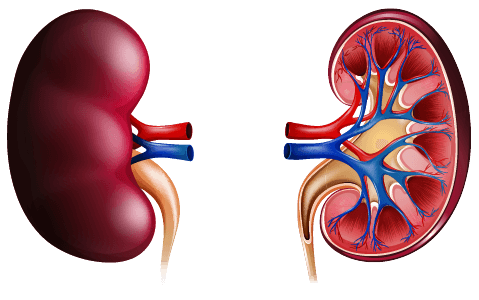
- The kidneys are enclosed in a fibrous capsule and consist of three main sections:
- The cortex – the outer section of the kidney containing nephrons, where blood is filtered.
- The medulla – the middle section of the kidney, where water is reabsorbed and urine is funnelled into the renal pelvis.
- The renal pelvis – the inner section of the kidney, where urine is collected before exiting via the ureter.
- The main blood vessels leading to and from the kidneys are:
- The renal arteries, which carry unfiltered blood to the kidneys from the heart.
- The renal veins, which carry filtered blood from the kidneys to the heart.
![]()
(Image: andrebuhrer, Pixabay)
(Header image: magicmine, Adobe Stock)