This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the processes involved in evolution by natural selection.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Outline the key stages in the evolutionary process.
- Explain why genetic variation and reproductive isolation are required for the evolution of new species.
- Discuss the role of mutation, natural selection and genetic drift in evolution.
- Describe speciation and adaptive radiation.
- Interpret a phylogenetic tree.

(Image: fprose, Pixabay)
Lesson Summary
- Evolution is the gradual genetic change of populations over time, that results in different forms and new species.
- Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection.
- He concluded that all life on Earth evolved from a common ancestor as a result of natural selection.
- Darwin’s theory provides a lens through which all biological processes can be viewed.
- The evolutionary process includes several key stages:
- Genetic variation.
- Genetic variation is created by mutation – the source of all new alleles – and enhanced in populations by sexual reproduction and gene flow.
- Reproductive isolation.
- Reproductive isolation is the separation of populations, which results in independent genetic changes.
- Natural selection, genetic drift and new mutations.
- Natural selection is the favouring of more suitable alleles over others.
- Genetic drift is the random change in allele frequencies due to chance.
- New mutations arise very slowly over time.
- Speciation.
- Speciation is the gradual differentiation of isolated populations into separate species.
- Adaptive radiation is the formation of multiple new species from a common ancestor.
- A phylogenetic tree (evolutionary tree) is a branching diagram showing the evolutionary relationships between different species.
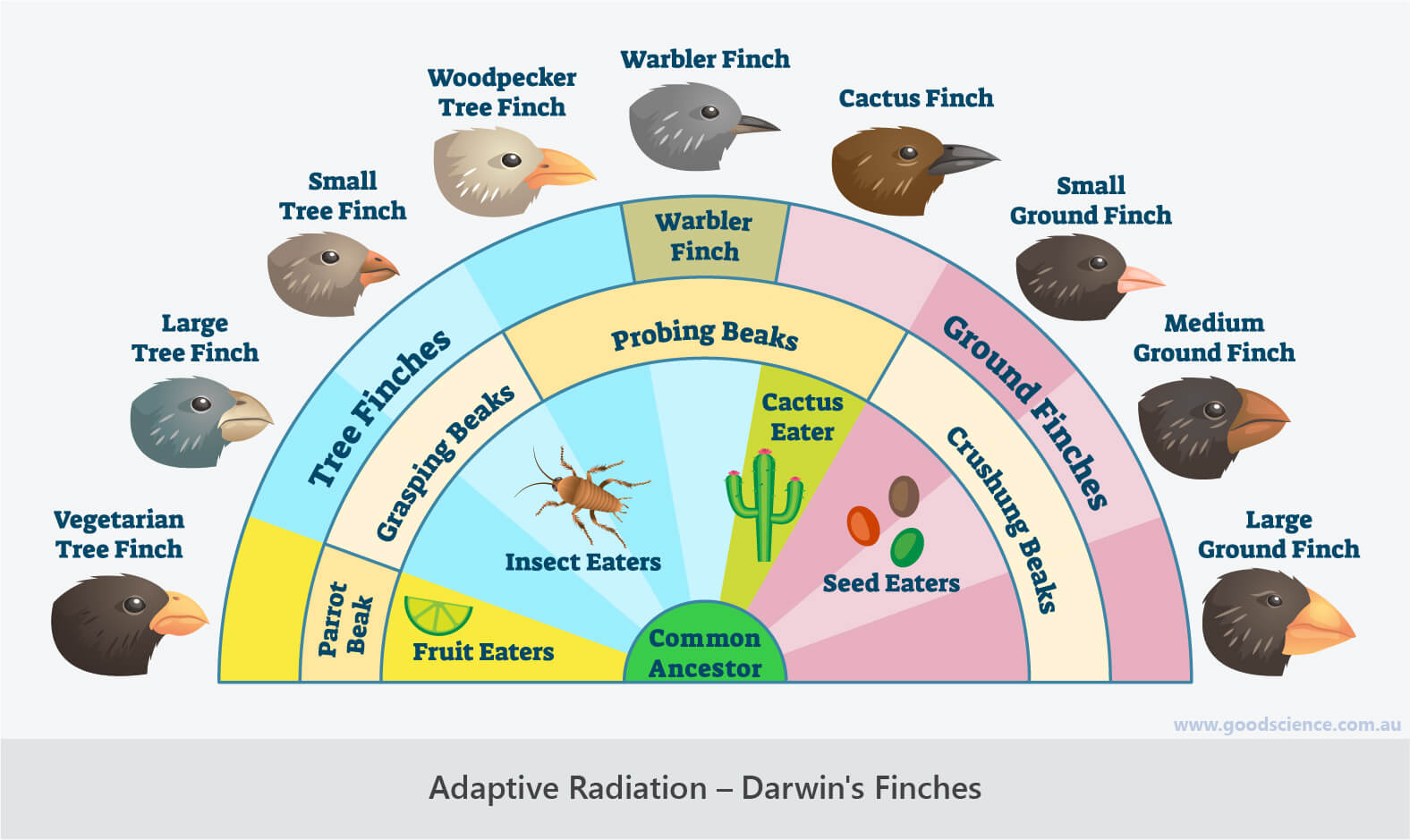
Darwin’s observations of the Galapagos finches helped solidify his theory of evolution.
(Image: VectorMine, Adobe Stock)
(Header image: Maridav, Adobe Stock)
