This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about classification systems for living and non-living things.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Give reasons for classifying things.
- Define ‘taxonomy’.
- Discuss how to choose criteria for classification systems.
- Describe how classification keys work, with examples.
- Discuss the limitations of classification systems.
(Images: blende12, Pixabay)
Lesson Summary
- Classification refers to the arrangement of things into different groups based on certain characteristics, and giving these groups labels.
- Taxonomy is the scientific classification of living things.
- Classification organises things in a way that makes it easier to identify, describe, remember, understand, communicate and predict information about them.
- Classification systems require meaningful criteria for distinguishing between different things so that those that are most similar are grouped together.
- Classification systems can change over time and there can be different classification systems for the same group of things.
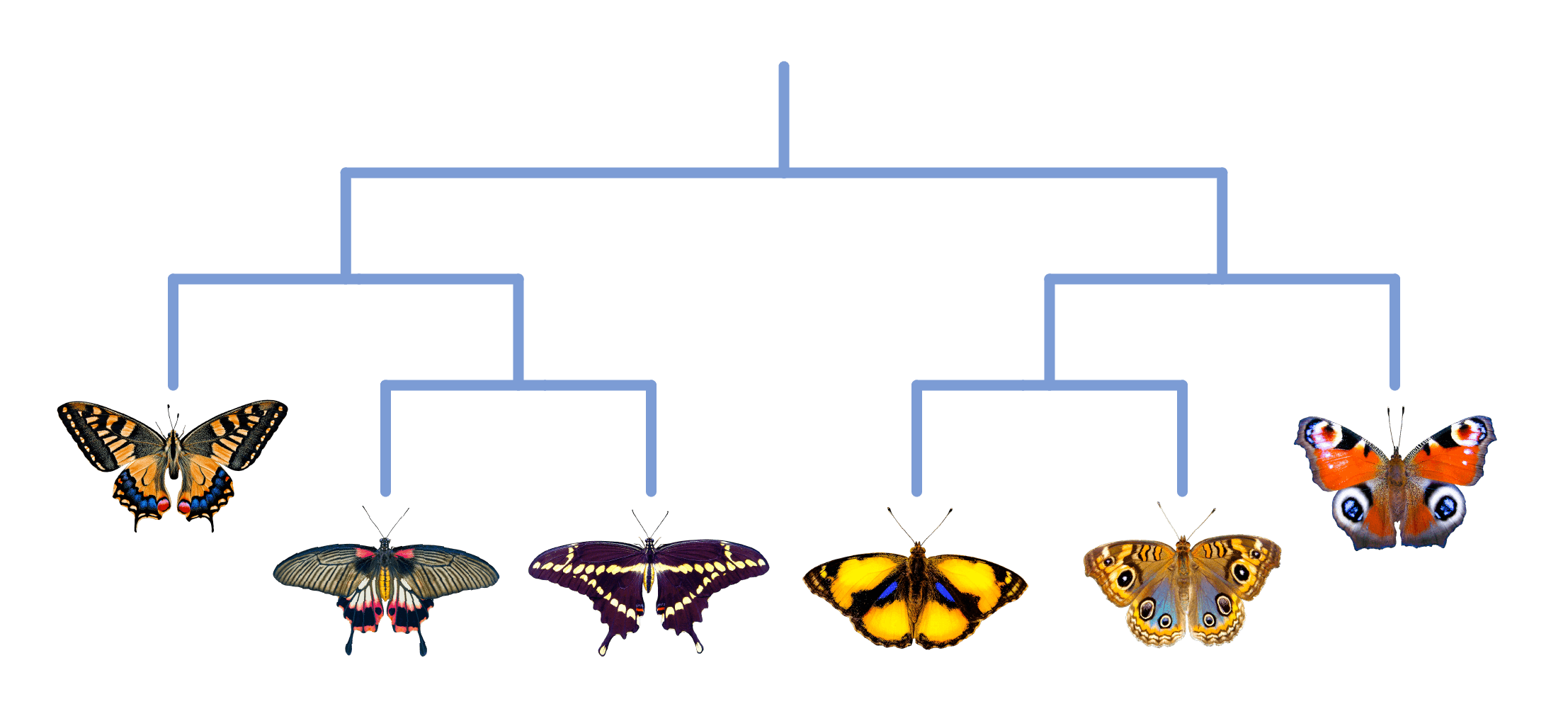
- A classification key involves a series of questions about the characteristics of something so that it can be correctly identified.
- A dichotomous key has two possible answers for each question, with the answers leading to further questions and ultimately the identification of the unknown thing.
- Dichotomous keys are usually represented as flow charts, but can also be represented as tabular keys or circular keys.
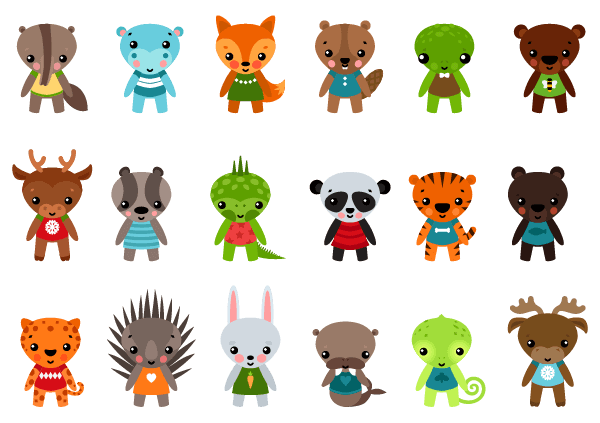

How could you distinguish between these animals?
(Image: Elegant Solution, Adobe Stock)
(Header image: blende12, Pixabay)
