This is a lesson summary. The full lesson can be viewed by purchasing an online course subscription.
Learning Objective
In this lesson we will learn about the arrangement of chromosomes in diploid and haploid cells, and how sex chromosomes determine biological sex.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Describe the arrangement of chromosomes in diploid cells (body cells) and haploid cells (sex cells), with examples.
- Distinguish between autosomal chromosomes and sex chromosomes.
- Describe how sex chromosomes determine biological sex in humans.
(Image: sinhyu, Adobe Stock)
Lesson Summary
- Chromosomes are structures located in the nuclei of cells that carry the cell’s genetic information.
- They are composed of DNA (genetic material) and protein (packaging material).
- Chromosomes are loosely packed during most of a cell’s life, but condense during cell division.
- Body cells (somatic cells) are diploid, which means they contain two sets of chromosomes, which exist in pairs known as homologous pairs.
- One chromosome in each pair is inherited from the mother and the other is inherited from the father.
- Sex cells (gametes) are haploid, which means they contain one set of chromosomes.
- Chromosomes contain sections inherited from both the mother and the father.
- The number of chromosomes in a cell varies between species.
- The haploid number is written as n and the diploid number is written as 2n.
- In humans, n = 23. Therefore, human sex cells contain 23 chromosomes and human body cells contain 46 chromosomes.
- Each set of chromosomes contains one sex chromosome.
- In humans, this is either an X chromosome or a Y chromosome.
- All other chromosomes are referred to as autosomal chromosomes (autosomes).
- Sex chromosomes determine the biological sex of an individual.
- Females have two X chromosomes (XX) in their body cells.
- Males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (XY) in their body cells.
- The sex chromosome carried by sperm cells determines the sex of offspring as egg cells always carry an X chromosome.
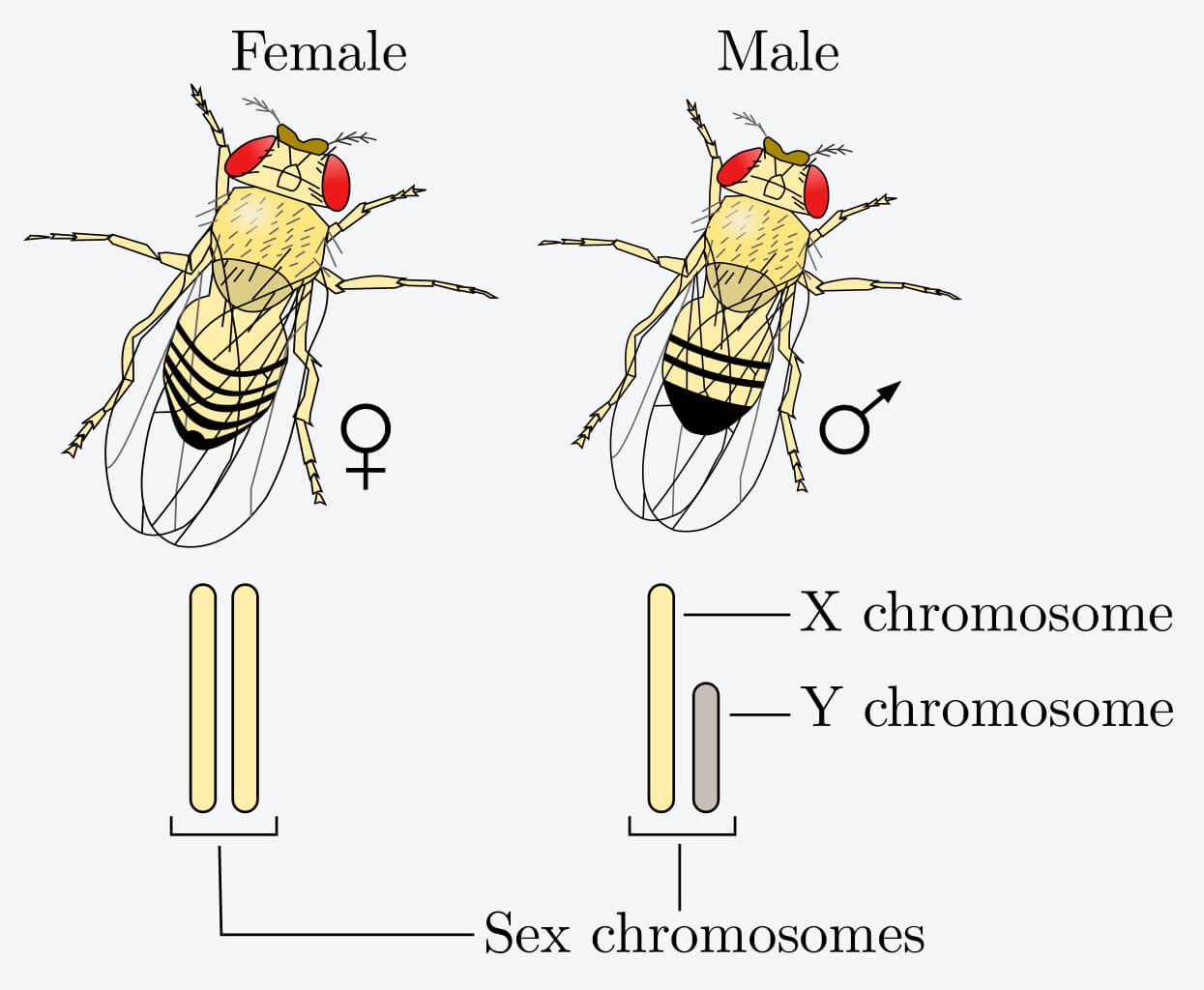
Sex determination in fruit flies (Drosophila) occurs in the same way as in humans.
(Image: YassineMrabet, Wikimedia Commons)
(Header image: ustas, Adobe Stock)