4 | Motion of the Planets
Motion of the Planets
- Planets move in two ways:
- They move in a path around the sun known as an orbit.
- They rotate on their axis – an imaginary line joining the north and south poles.
- The time taken for a planet to orbit the sun is known as a year.
- A year on Earth is approximately 365 days.
- The further a planet is from the sun, the longer its year. This is due to two factors:
- The further a planet is from the sun, the larger its orbit.
- The further a planet is from the sun, the smaller the effect of gravity, meaning the sun has less of a pull on the planet, resulting in a slower orbital speed.
- The time taken for a planet to rotate on its axis is known as a day.
- A day on Earth is approximately 24 hours.
- The rotational speed of a planet is largely determined by the initial rotational speed when the planet was formed. Therefore, the length of a day is unrelated to the size of a planet’s orbit, the orbital speed or the size of a planet.
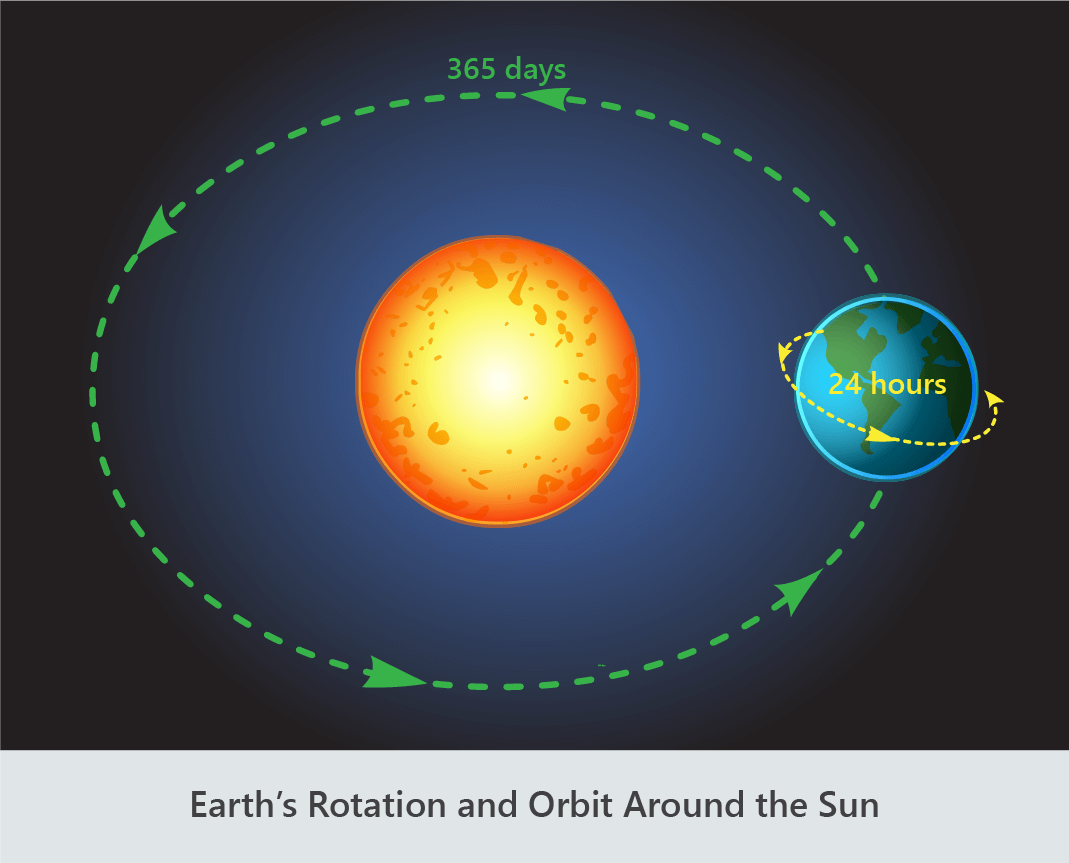
Earth takes a day to rotate on its axis and a year to orbit the sun.
(Image: LuckySoul, Adobe Stock)
- The lengths of days and years for the eight major planets are shown in the table below (in Earth hours/days/years).
| Planet | Day | Year |
| Mercury | 1,408 hours (59 days) | 88 days |
| Venus | 5,832 hours (243 days) | 225 days |
| Earth | 24 hours | 365 days |
| Mars | 25 hours | 687 days (1.9 years) |
| Jupiter | 10 hours | 4,333 days (12 years) |
| Saturn | 11 hours | 10,759 days (29 years) |
| Uranus | 17 hours | 30,687 days (84 years) |
| Neptune | 16 hours | 60,190 days (165 years) |
The lengths of days and years on the planets of our solar system

